Authn & Authz using OPA & Envoy Part 2
Introduction
So in part 1 we introduced what we're doing, created our app registrations within Azure AD and retrieved our token, now we'll look to continue with our PoC & test it out.
Implement
I'm probably about to present the scenario in the worst possible way...
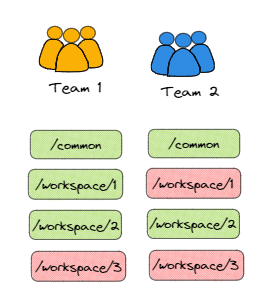
But what we want is for the teams to authenticate using their respective tokens.
What the teams have access to is determined by our team role, so the roles and endpoints shown in the diag below is what we will look to create.
Note: Green is permit, red is deny..
API
In our repo here, we have a dir called dummy-api, its a quick and nasty Fast API which has a couple of endpoints.
dummy-api/main.py:
@app.get("/common")
def common():
return {"message": "common"}
@app.get("/workspaces/{id}")
def namespace(id):
return {"message": f"You have access to workspace {id}"}
@app.get('/health')
def health():
return 'health'
If I were to call /common endpoint, I'd get the response {"message": "common"}.
If I call /workspaces/1 I would get the response {"message": "You have access to workspace 1"}.
In our Dockerfile, we are just copying and running our app, on port 8080.
dummy-api/Dockerfile:
FROM python:slim
RUN pip install fastapi \
pip install uvicorn
WORKDIR /app
COPY dummy-api/main.py /app
CMD ["uvicorn", "main:app", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "8080"]
Finally we define our pod in our docker-compose, and add a port-forward so we can test it out:
docker-compose.yml
services:
dummy-api:
image: dummy-api
build:
context: .
dockerfile: dummy-api/Dockerfile
ports:
- "8080:8080"
If we run docker-compose up the pod should run and be exposed on port 8080
Lets try a get request to our workspaces endpoint: http://localhost:8080/workspaces/1
{
"message": "You have access to workspace 1"
}
Envoy
Ok so lets add in our AuthN, remember we're using Envoy here to handle this, it will act as a proxy for our service and should validate this token against Azure AD.
We'll need to put our yaml engineering hats on for this....
We'll want to configure some static_resources specifically listeners & clusters
envoy/config.yaml:
static_resources:
listeners:
- address:
socket_address:
address: 0.0.0.0
port_value: 8000
Here we're simply declaring that we're listening on port 8000, next we'll add a filter so we can specify a route and decide what to do once that route has been matched.
envoy/config.yaml:
filter_chains:
- filters:
- name: envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.network.http_connection_manager.v3.HttpConnectionManager
codec_type: auto
stat_prefix: ingress_http
route_config:
name: local_route
virtual_hosts:
- name: backend
domains:
- ["*"]
routes:
- match:
prefix: "/"
route:
cluster: service
http_filters:
- name: envoy.filters.http.jwt_authn
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.http.jwt_authn.v3.JwtAuthentication
providers:
provider_azad:
issuer: https://login.microsoftonline.com/<TenantID>/v2.0
audiences: <ClientID>
forward: true
remote_jwks:
http_uri:
uri: "https://login.microsoftonline.com/<TenantID>/discovery/v2.0/keys"
cluster: azad
timeout: 10s
cache_duration:
seconds: 600
rules:
- match:
prefix: /health
- match:
prefix: /common
requires:
provider_and_audiences:
provider_name: provider_azad
audiences:
<ClientID>
- match:
prefix: /workspaces
requires:
provider_and_audiences:
provider_name: provider_azad
audiences:
<ClientID>
So we've done quite a bit here...
We're specifying that we want to match all domains [*] with routes / and we want to route it to a cluster named service.
On top of this we've added a http_filter which will carry out our authn, this will be routed to our azad cluster.
In the filter we provide the tenant id and aud of our my-demo-app app registration.
We've also added in some rules to match against, now I could probably do this better, like incorporate regex, but I didn't quite get that working, so all we're specifying is /common and /workspaces require token validating.
My health endpoint however does not have provider_and_audiences defined, thus allows for unauthenticated requests.
Under the http_filters: we'll also add our authz filter.
envoy/config.yaml:
- name: envoy.ext_authz
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.http.ext_authz.v3.ExtAuthz
transport_api_version: V3
with_request_body:
max_request_bytes: 8192
allow_partial_message: true
failure_mode_allow: false
grpc_service:
google_grpc:
target_uri: opa:9191
stat_prefix: ext_authz
Key thing to note here is our target uri which is opa, and the plugins.envoy_ext_authz_grpc.addr we supply to our OPA pod, Im going to use 9191, we'll need to specify set this in our docker-compose later when we setup OPA.
Note there is a envoy.filters.http.router which just propagates requests to correct cluster.
Now we declare our clusters, service and azad respectively. Both of these require an address and port number, in the case of our dummy-api its the service name we specified in our docker-compose.
For azad cluster it will be the Azure AD login page login.microsoftonline.com.
envoy/config.yaml:
clusters:
- name: service
connect_timeout: 0.25s
type: strict_dns
lb_policy: round_robin
load_assignment:
cluster_name: service
endpoints:
- lb_endpoints:
- endpoint:
address:
socket_address:
address: dummy-api
port_value: 8080
- name: azad
connect_timeout: 100s
type: strict_dns
lb_policy: round_robin
load_assignment:
cluster_name: azad
endpoints:
- lb_endpoints:
- endpoint:
address:
socket_address:
address: login.microsoftonline.com
port_value: 443
transport_socket:
name: envoy.transport_sockets.tls
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.transport_sockets.tls.v3.UpstreamTlsContext
sni: login.microsoftonline.com
Now under services we're going to add our envoy services, mounting the config.yaml file and port-forwarding to the listeners.
docker-compose.yml
envoy:
image: envoyproxy/envoy:v1.23-latest
volumes:
- ./envoy/config.yaml:/etc/envoy/envoy.yaml
ports:
- "5200:8000"
- "5201:8001"
OPA
Ok for OPA all we need is a simple policy.rego file, remember example is in the repo.
So I'm going to just paste in th rego with inline comments, as hopefully its self explanatory
package envoy.authz
# Importing required modules
import input.attributes.request.http as http_request
import input.parsed_path
# Default deny policy
default allow = false
# Rule to allow GET requests to path starting with "health"
allow {
parsed_path[0] == "health"
http_request.method == "GET"
}
# Rule to allow GET requests to path starting with "common"
allow {
parsed_path[0] == "common"
http_request.method == "GET"
}
# Rule to check required roles for accessing resource
allow {
required_roles[r]
}
# Rule to define required roles for accessing resource
required_roles[r] {
perm := role_perms[claims.roles[r]][_]
perm.method = http_request.method
perm.path = http_request.path
}
# Decoding JWT bearer token and extracting claims
claims := payload {
[_, payload, _] := io.jwt.decode(bearer_token)
}
# Extracting JWT bearer token from authorization header
bearer_token := t {
v := http_request.headers.authorization
startswith(v, "Bearer ")
t := substring(v, count("Bearer "), -1)
}
# Mapping of roles to permissions
role_perms = {
"team1": [
{"method": "GET", "path": "/workspaces/1"},
{"method": "GET", "path": "/workspaces/2"},
],
"team2": [
{"method": "GET", "path": "/workspaces/2"},
],
}
Now under services we're going to add our OPA service, mounting the rego file and remembering to set our plugins.envoy_ext_authz_grpc.addr to 9191.
docker-compose.yml
opa:
image: openpolicyagent/opa:latest-envoy
volumes:
- ./opa/policy.rego:/etc/policy.rego
command:
- run
- --server
- --log-level=debug
- --log-format=json-pretty
- --set=plugins.envoy_ext_authz_grpc.addr=:9191
- --set=decision_logs.console=true
- --set=plugins.envoy_ext_authz_grpc.path=envoy/authz/allow
- /etc/policy.rego
Test
With all our services defined and policies in place, I'm just going run docker-compose up
We should see our pods running, now lets do a GET request to http://localhost:5200/common
# REQ:
curl http://localhost:5200/common
# RESP:
401 Unauthorized
Jwt is missing
Good so as expected when there isn't a token provided envoy will return a 401.
Token time
Lets retrieve our token for Team 1 and add that in our request:
# REQ:
curl http://localhost:5200/common -H "Authorization: Bearer eyJ0eXAiOi..."
# RESP:
200
{
"message": "common"
}
Now lets try access workspace 1 & 2:
# REQ:
curl http://localhost:5200/workspaces/1 -H "Authorization: Bearer eyJ0eXAiOi..."
# RESP:
200
{
"message": "You have access to workspace 1"
}
# REQ:
curl http://localhost:5200/workspaces/2 -H "Authorization: Bearer eyJ0eXAiOi..."
# RESP:
200
{
"message": "You have access to workspace 2"
}
All good so far... Workspace 3?
# REQ:
curl http://localhost:5200/workspaces/3 -H "Authorization: Bearer eyJ0eXAiOi..."
# RESP:
403

As expected Team 1 is forbidden from accessing workspace 3!
And carrying out the same validation for Team2 (remember to update the credentials when retrieving the token).
We should get 200 for /common and /workspaces/2, and a 403 for everything else.
Conclusion
We've successfully implemented Authentication and Authorisation via a quick PoC using OPA and Envoy.
There are no doubt improvements to be made to both policies and envoy configuration, but hopefully this was a useful quick go to for getting started.
 Useful
Useful